What are the angle measures in triangle abc – In geometry, understanding the angle measures in a triangle is fundamental to comprehending the properties and relationships within triangles. This exploration delves into the Angle Sum Theorem, techniques for measuring angles, triangle classification based on angle measures, angle bisectors and trisectors, special triangles, and practical applications of angle measurements in various fields.
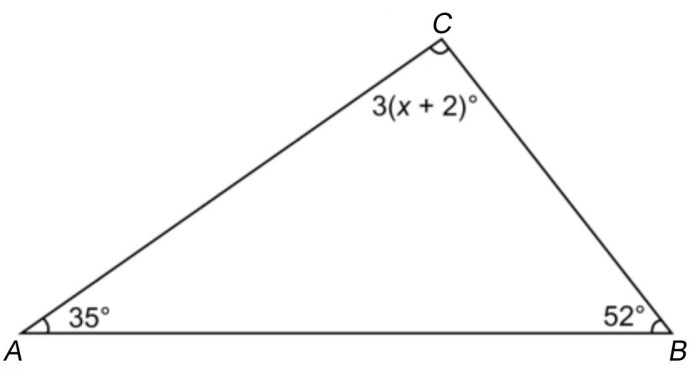
The Angle Sum Theorem establishes the cornerstone for understanding angle measures in triangles. It asserts that the sum of the interior angles of any triangle is 180 degrees, providing a valuable tool for verifying and calculating unknown angle measures.
Angle Sum Theorem: What Are The Angle Measures In Triangle Abc
The Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. This theorem holds true for all triangles, regardless of their shape or size.
For example, consider a triangle with angles A, B, and C. According to the Angle Sum Theorem, the sum of these angles is 180 degrees: A + B + C = 180 degrees.
Measuring Angles in a Triangle
There are several tools and methods that can be used to measure the angles of a triangle. One common tool is a protractor, which is a semicircular device with a scale marked in degrees.
To use a protractor to measure an angle, place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle and align the baseline with one of the sides of the angle. The scale on the protractor will indicate the measure of the angle.
Other methods for measuring angles in a triangle include using a compass and straightedge or using trigonometry.
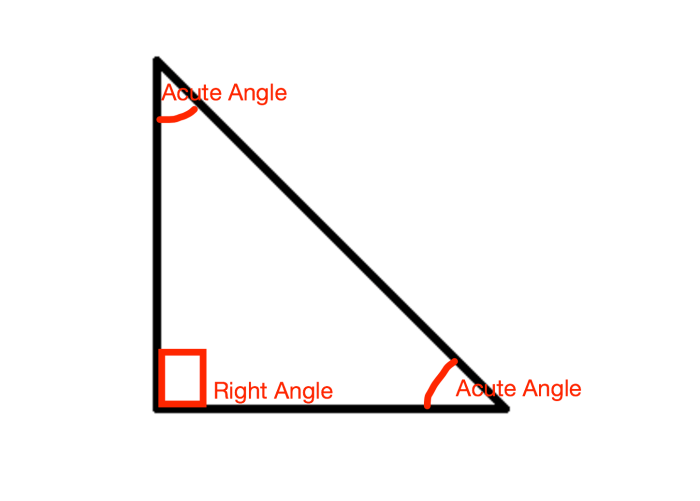
Classifying Triangles by Angle Measures
Triangles can be classified into different types based on the measures of their angles. The three main types of triangles are:
- Acute triangleshave all three angles less than 90 degrees.
- Right triangleshave one angle equal to 90 degrees.
- Obtuse triangleshave one angle greater than 90 degrees.
Equilateral triangles are a special type of triangle in which all three angles are equal to 60 degrees.
Angle Bisectors and Angle Trisectors
An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two equal parts. To construct an angle bisector, use a compass and straightedge to draw a circle centered at the vertex of the angle. The two points where the circle intersects the sides of the angle are the points on the angle bisector.
Angle trisectors are lines that divide an angle into three equal parts. Constructing angle trisectors is more complex than constructing angle bisectors and requires using more advanced geometry.
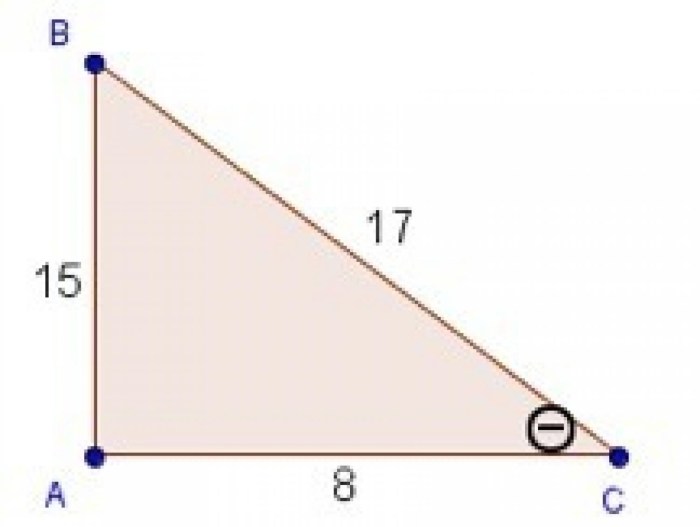
Special Triangles and Their Angle Measures, What are the angle measures in triangle abc
There are several types of special triangles that have unique angle measures. Two common types of special triangles are:
- Isosceles triangleshave two equal sides and two equal angles.
- Equilateral triangleshave all three sides and all three angles equal.
The 30-60-90 triangle is a special right triangle with angles of 30 degrees, 60 degrees, and 90 degrees.
Applications of Angle Measures in Triangles
Angle measures in triangles have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: Angle measures are used to design buildings and other structures.
- Engineering: Angle measures are used to design bridges, machines, and other structures.
- Surveying: Angle measures are used to determine the boundaries of land.
- Navigation: Angle measures are used to determine the direction of travel.
Understanding angle measures in triangles is essential for solving problems and making accurate calculations in these and other fields.
Top FAQs
What is the Angle Sum Theorem?
The Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
How do I measure the angles of a triangle?
You can use a protractor, compass, or straightedge to measure the angles of a triangle.
What is an angle bisector?
An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two equal parts.
What is a special triangle?
A special triangle is a triangle that has specific angle measures or side lengths, such as an equilateral triangle or a 30-60-90 triangle.