Nursing diagnosis for myasthenia gravis – Myasthenia gravis, a chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction, poses significant challenges for patients and healthcare professionals. This article provides an in-depth exploration of nursing diagnoses for myasthenia gravis, encompassing assessment, care planning, patient education, and support.
Understanding the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and diagnostic tests associated with myasthenia gravis is crucial for accurate nursing assessment. Comprehensive physical examinations, including neuromuscular assessments, and diagnostic tests, such as electromyography and nerve conduction studies, aid in confirming the diagnosis.
1. Definition and Overview of Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction, leading to weakness and fatigue in skeletal muscles. It is caused by a defect in the transmission of nerve impulses to muscles, resulting in impaired muscle function.
The underlying pathophysiology involves the production of autoantibodies that target the acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on the postsynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction. These autoantibodies block or destroy the AChRs, disrupting the normal transmission of nerve signals and leading to muscle weakness.
Myasthenia gravis can manifest with a wide range of clinical symptoms, including:
- Muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves with rest
- Drooping eyelids (ptosis)
- Double vision (diplopia)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Difficulty breathing (respiratory muscle weakness)
2. Nursing Assessment for Myasthenia Gravis
A comprehensive nursing assessment is crucial for early detection and management of myasthenia gravis. It involves:
- Detailed history: Collecting information about the patient’s symptoms, duration, and progression, as well as any potential triggers or exacerbating factors.
- Physical examination: Performing a thorough neuromuscular assessment, including:
- Muscle strength testing using the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale
- Ocular examination for ptosis and diplopia
- Respiratory assessment for signs of muscle weakness
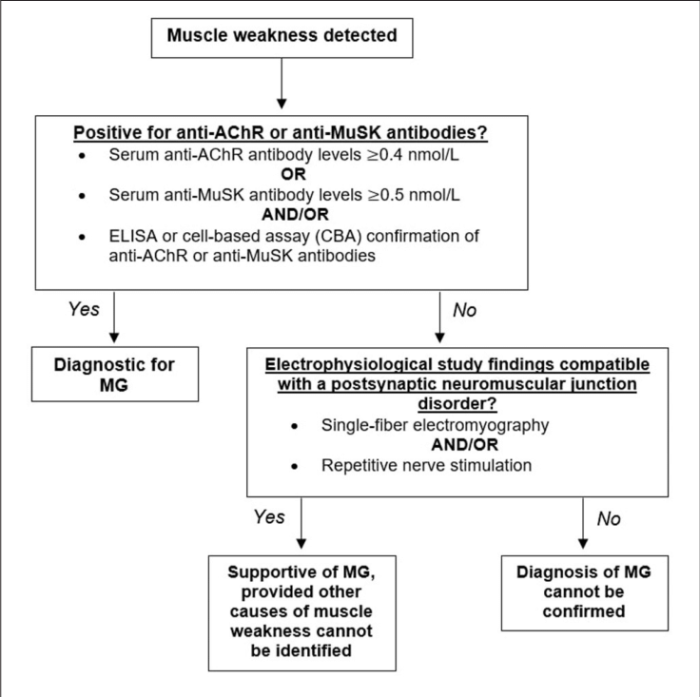
- Diagnostic tests: Collaborating with the healthcare team to order and interpret relevant diagnostic tests, such as:
- Repetitive nerve stimulation (RNS) and single-fiber electromyography (SFEMG)
- Anti-AChR antibody testing
- CT or MRI imaging to rule out other neurological conditions
3. Nursing Diagnoses for Myasthenia Gravis: Nursing Diagnosis For Myasthenia Gravis

Common nursing diagnoses associated with myasthenia gravis include:
- Impaired Physical Mobilityrelated to muscle weakness
- Ineffective Airway Clearancerelated to respiratory muscle weakness
- Risk for Aspirationrelated to dysphagia
- Disturbed Body Imagerelated to visible muscle weakness and drooping eyelids
- Deficient Knowledgerelated to the condition, its management, and potential complications
4. Nursing Care Planning for Myasthenia Gravis

| Nursing Diagnosis | Goals | Interventions | Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impaired Physical Mobility | Patient will maintain optimal mobility and independence. | – Assist with activities of daily living as needed.
|
– Patient demonstrates improved mobility and independence.
|
| Ineffective Airway Clearance | Patient will maintain a patent airway and adequate respiratory function. | – Monitor respiratory status closely.
|
– Patient maintains a clear airway and adequate oxygen saturation.
|
| Risk for Aspiration | Patient will remain free from aspiration events. | – Assess swallowing ability and provide modified diets as needed.
|
– Patient swallows safely and effectively without aspiration.
|
5. Patient Education and Support for Myasthenia Gravis
Patient education is vital in managing myasthenia gravis. It includes:
- Medication management: Informing patients about their medications, their side effects, and the importance of adherence.
- Lifestyle modifications: Encouraging patients to adopt energy-conserving techniques, such as pacing activities and avoiding triggers.
- Symptom management strategies: Teaching patients about managing muscle weakness, fatigue, and other symptoms.
Support systems are also crucial for patients with myasthenia gravis. These may include:
- Support groups: Connecting patients with others who understand their experiences and challenges.
- Social services: Providing assistance with financial aid, transportation, and other resources.
- Online forums and communities: Facilitating communication and support among patients and caregivers.
FAQ Guide
What are the common nursing diagnoses for myasthenia gravis?
Impaired physical mobility, ineffective airway clearance, risk for aspiration, and impaired swallowing are common nursing diagnoses associated with myasthenia gravis.
How is myasthenia gravis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a comprehensive nursing assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, including electromyography and nerve conduction studies.
What are the goals of nursing care for myasthenia gravis?
Nursing care aims to improve physical mobility, maintain airway patency, prevent aspiration, and enhance overall patient well-being through evidence-based interventions and patient education.