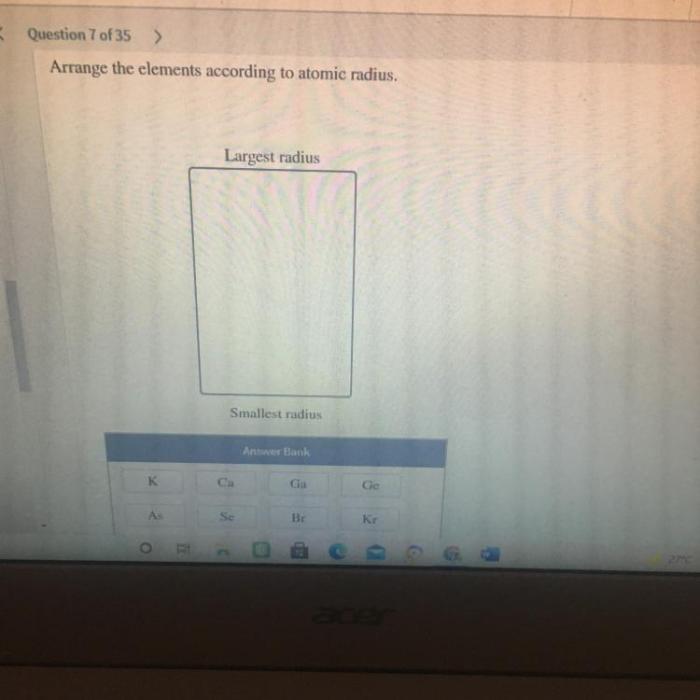
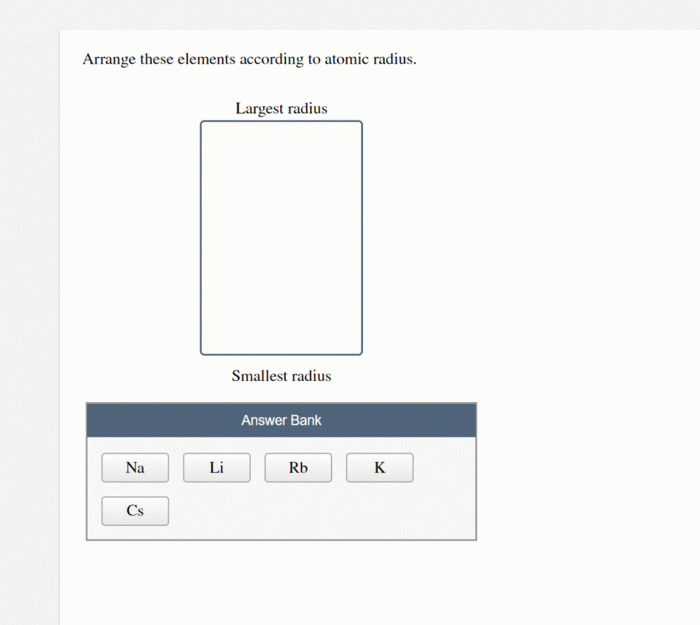
Arrange these elements according to atomic radius. – Arrange these elements according to atomic radius, delving into the captivating world of atomic structure. Atomic radius, a fundamental property of elements, holds immense significance in determining their chemical and physical behavior. This exploration unravels the factors influencing atomic radius, its trends across the periodic table, and its diverse applications in scientific fields.
Understanding atomic radius provides a deeper comprehension of element properties, enabling researchers to tailor materials with specific characteristics and harness their potential in various technological advancements.
Atomic Radius
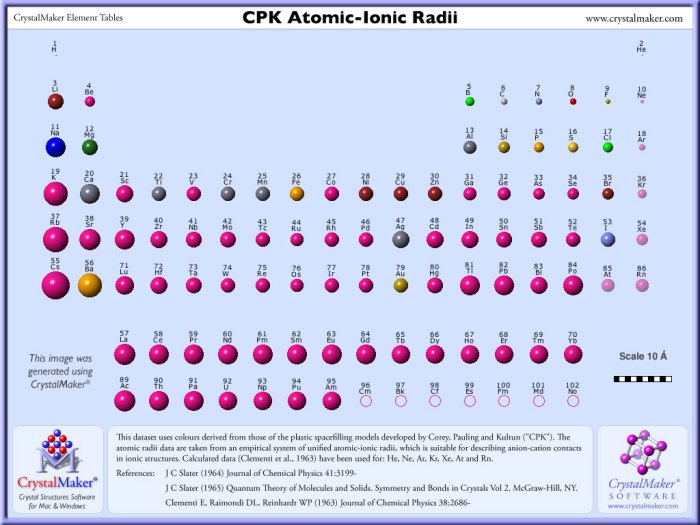
Atomic radius is a measure of the size of an atom. It is defined as the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.
Several factors affect atomic radius, including the number of protons in the nucleus, the number of electrons in the atom, and the shielding effect of inner electrons.
Methods for Arranging Elements
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties.
Atomic radius trends can be observed across periods and groups of the periodic table. In general, atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.
Examples of Atomic Radius Trends
- The alkali metals have the largest atomic radii in their respective periods.
- The noble gases have the smallest atomic radii in their respective periods.
- The atomic radius of an element increases as the number of electron shells increases.
Applications of Atomic Radius Data, Arrange these elements according to atomic radius.
Atomic radius data is used in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology.
In chemistry, atomic radius data is used to predict the chemical properties of elements and to understand the formation of chemical bonds.
In materials science, atomic radius data is used to design and develop new materials with specific properties.
In nanotechnology, atomic radius data is used to create nanostructures with precise dimensions.
Detailed FAQs: Arrange These Elements According To Atomic Radius.
What factors affect atomic radius?
Atomic radius is primarily influenced by the number of electron shells and the effective nuclear charge experienced by the outermost electrons.
How does atomic radius vary across the periodic table?
Atomic radius generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.
What are some applications of atomic radius data?
Atomic radius data finds applications in predicting crystal structures, designing materials with specific properties, and understanding chemical reactivity.